Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy gains traction
A challenge with materials-based PDT is that the production process has to allow for coating on even complex geometries.
The ALD/MLD technique may be a suitable tool to produce high-quality novel materials for possible applications in antimicrobial PDT.

Killing off bacteria by using light on a thin film covering sounds intriguing to say the least. The possibilities would be endless, from restorations to self-cleaning environmental surfaces, and on. A collaborative team from NIOM and the University of Oslo (UiO) is currently making strides in this direction.
– The principle of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (PDT) is appealing because it can be controlled by an external light source and possibly the use of durable materials, says Ellen Bruzell.
Bruzell is senior scientist at NIOM. She is one of the co-authors of a recent study, together with lead investigator Melania Rogowska (UiO), senior scientist Håkon Valen (NIOM) and Professor Ola Nilsen (UiO).
– One challenge with materials-based PDT is that the production process has to allow for coating on even complex geometries, Bruzell says.
The team therefore explored the ability of the emerging atomic/molecular layer deposition (ALD/MLD) technique to produce and tune PDT active materials.
Results
– The study found that films based on the 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid linker and zirconium (Zr) clusters reduced the number of viable bacteria by 99.9%, Bruzell says.
Two other photoactive systems tested did not show any apparent antibacterial activity. These were based on the 2,5-dihydroxy-1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid and 2-amino-1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid linkers. All three are photoactive Zr-organic hybrid thin films made by MLD and were combined with ZrCl4 to produce hybrid coatings.
– This means that the ALD/MLD technique may be a suitable tool to produce high-quality novel materials for applications in antimicrobial PDT. However, it requires a careful selection of aromatic ligands used to construct photoactive materials, Rogowska says.
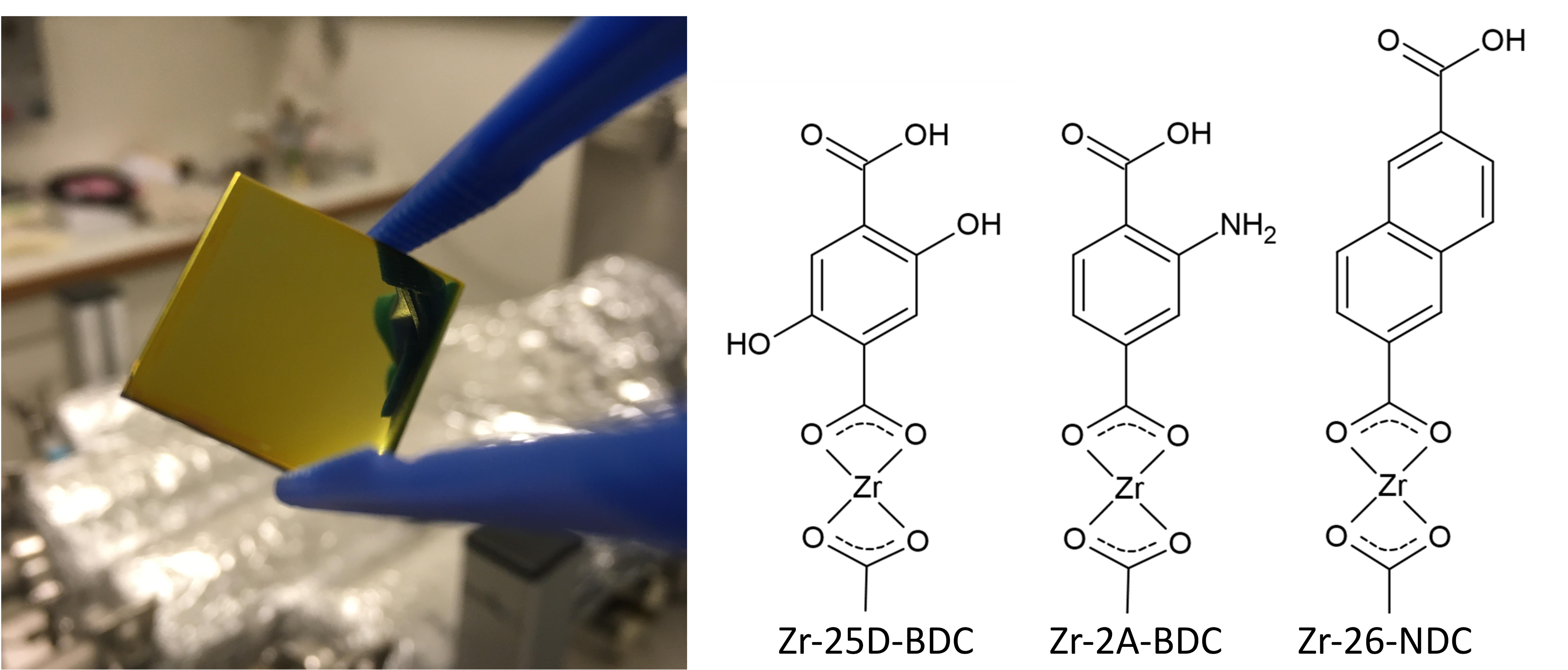
Illustration by Melania Rogowska, University of Oslo. Rogowska is currently a guest researcher at NIOM.
Photoactive Zr-aromatic hybrid thin films made by molecular layer deposition
Rogowska M, Bruzell E, Valen H, Nilsen O
Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) Advances, 2022, 12, 15718–15727
DOI: 10.1039/d2ra02004a
NIOM Newsletter August 2022
